|
IB Business Management:
1.1 What is a business? This topic introduces IB Business Management. It explains what a business is and what businesses do. It outlines the main business functions and explains the different sectors of industry. Entrepreneurship and the reasons for setting up a business are examined, as too are the challenges and opportunities that arise when establishing a business.
|
|
Key learning outcomes:
|
What is a business?A business is any activity that provides goods or services to consumers for the purpose of making a profit. Examples of goods provided by a business are tangible items such as cars, televisions, or soda. A service is an action or work performed for monetary compensation. Services include things such as haircuts, hotel stays, or roller-coaster rides. Not for profit organisations are classified as businesses.
|
What do businesses do?Businesses identify the needs of consumers or other firms. They then purchase resources, which are the inputs of the business or factors of production, in order to produce output. The 'outputs' of a business are the goods and services that satisfy consumers' needs, usually with the aim of making a profit.
|
Starting a business: the role of the entrepreneurAn entrepreneur is someone who takes the financial risk (and reaps the rewards!) of starting and managing a new venture. These people have:
Qualities of an entrepreneur
Why start a business? Reasons to start a business include:
|
What is an entrepreneur?How to start a business |
Problems faced by start-upsEven if an entrepreneur has all of the right qualities, success with a new business can never be guaranteed. Many businesses fail during the first year of operation, because of:
Essential statement: The reasons for business failure could apply at any stage of the development of a business, but the first few months are the riskiest of all. |
Are you an entrepreneur? Take the quiz to find out! |
Teach everyone to start a business |
Everyone can now be an entrepreneur |
Starting your own business: summary notesSummary notes on the reasons for starting up a business, common steps in the process of business start up, and the problems associated with starting anew business (including reasons why most new business will not last 18 months).
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
Top tips for starting a business |
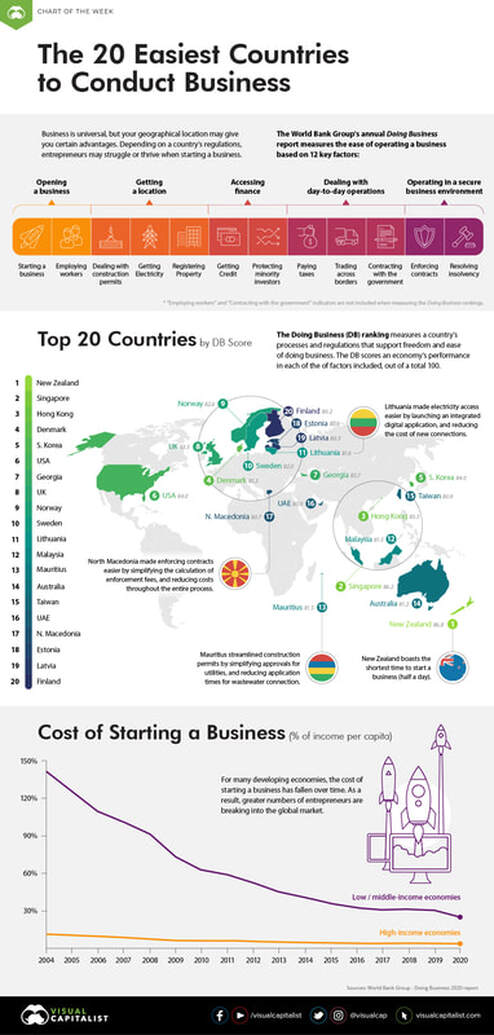
Best countries to be in business |
The business planThe business plan is a written document that describes a business, its objectives and its strategies, the market it is in and its financial forecasts
The contents of a typical business plan include:
The single biggest reason why a start-up succeeds |
Do you need a business plan? |
Adventures of the mini-entrepreneur
A cute animated series about a budding entrepreneur
|
|
|
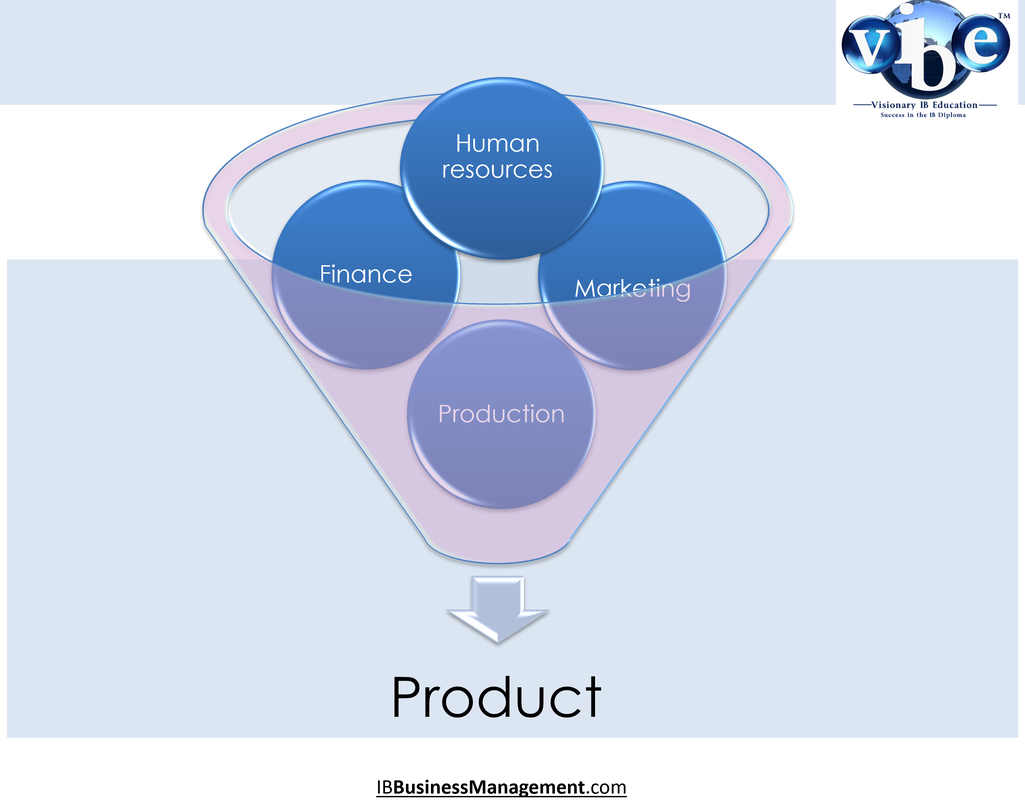
Business functionsMost businesses have four functional departments: Marketing, Human Resources, Finance and Production. These will be staffed by people with specific qualifications skills and experience in the work of the functional areas. A small business entrepreneur may have to cover all of these functions by themselves or outsource these functions to specialist firms.
MarketingThe commercial processes involved in creating and designing, promoting and selling and distributing a product or service. The management task that links the business to the customer by identifying and meeting the needs of customers profitably. It does this by getting the right product at the right price at the right place with the right promotion.
Human Resource ManagementThe process of determining human resource needs and then recruiting, selecting, developing, motivating, evaluating, compensating, and scheduling employees to achieve organisational objectives.
FinanceFinance is the management of money and credit and banking and investments. The accounts and finance section also provides the business with an array of tools for keeping track of cash flows, judging the viability of an investment and being able to prepare and analyse a financial records to both report on and evaluate the health of a business.
|
Operations ManagementSometimes referred to as production. Operations management is concerned with supervising, designing and controlling the procedures of the production process. It is the management of processes used to design, supply, produce, and deliver goods and services to customers.
What is profit? |
Capital goodsGoods used in the production of other goods and services.
|
Opportunity costOne of the most important business concepts to understand.
|
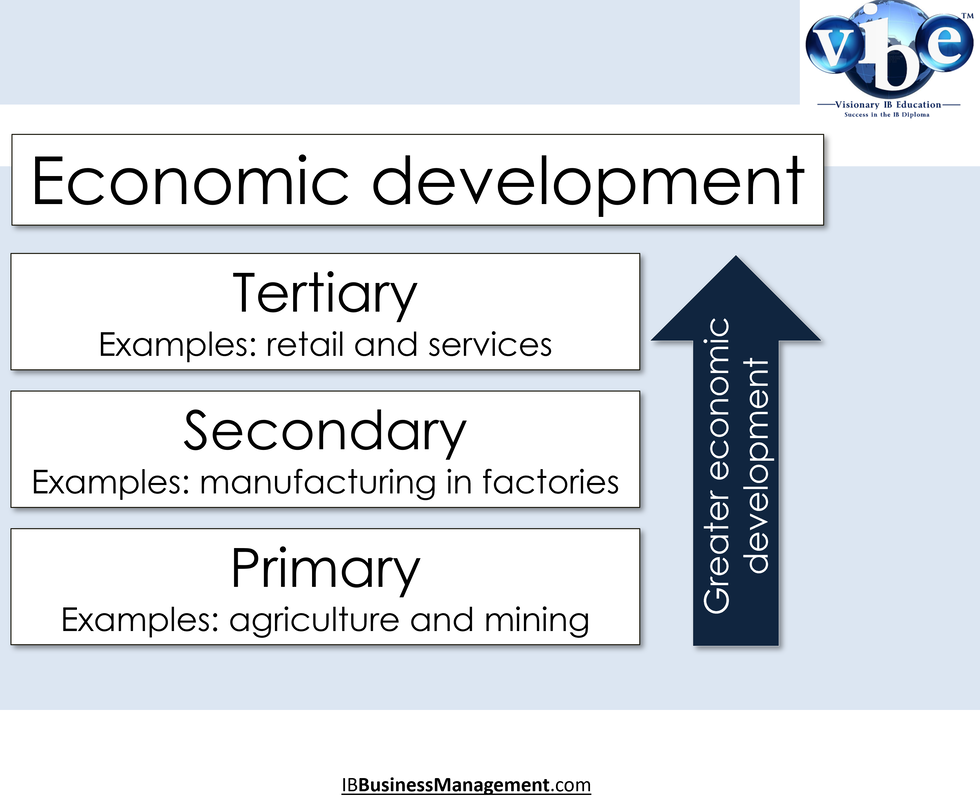
Sectors of industry
All production can be classified into three broad types of business activity, or sectors of industry: primary, secondary and tertiary sectors – the quarternary sector is a specialised area of services based on providing knowledge services.
Primary sectorPrimary Sector: This sector deals with the extraction and harvesting of natural resources such as agriculture and mining.
Tertiary sectorTertiary Sector: Retailers, hospitality, entertainment, and financial companies make up this sector. These companies provide services to consumers.
|
Secondary sectorSecondary Sector: This sector comprises construction, manufacturing, and processing. Basically, this sector comprises industries that relate to the production of finished goods from raw materials.
Quaternary sectorQuaternary Sector: The final sector deals with knowledge or intellectual pursuits including research and development (R&D), business, consulting services, and education.
|
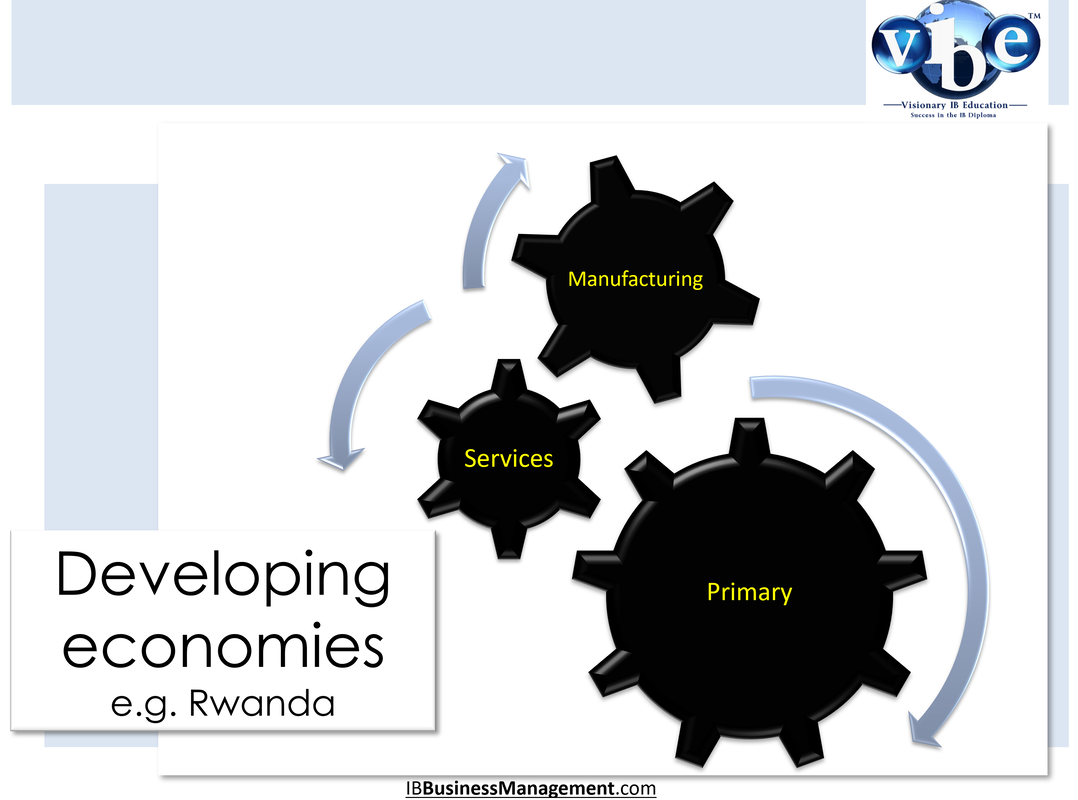
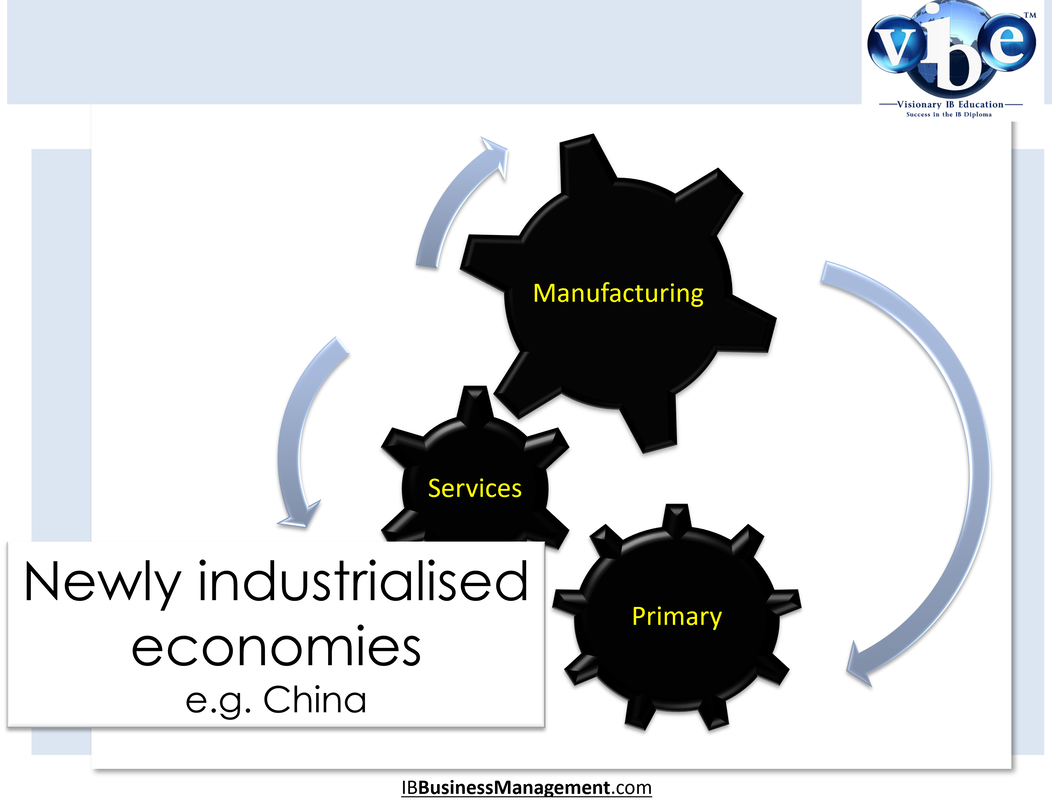
Sectors and changes in sectorsThe main focus of an economy's activity shifts from the primary, through the secondary and finally to the tertiary sector. Countries with a low per capita income are in an early state of development; the main part of their national income is achieved through production in the primary sector. Countries in a more advanced state of development, with a medium national income, generate their income mostly in the secondary sector. In highly developed countries with a high income, the tertiary (and quaternary) sector dominates the total output of the economy.
|
Not-for-profit organisationsIf an organisation is taking resource inputs (e.g. labour and capital) and then turning it into outputs (e.g. feeding the hungry) they are, by definition, a business. A charity will use the time of volunteers and paid help and use the charitable donations to produce services which fulfill the objectives of the organisation.
The difference between not-for-profits and charities |
Economic developmentProduction and employment tends to shift from primary through to secondary through to tertiary the more developed an economy becomes.
Developing countriesDeveloping countries such as Rwanda and Bangladesh will have the bulk of their economic activity concentrated in primary industries such as farming and mining. Manufacturing will be developing and service sector industries will be in their infancy.
Newly industrialised economiesOverall economic activity has significantly increased in newly industrialised economies (sometimes termed ‘emerging markets’). Manufacturing industries expand to a relatively large share of overall economic activity, often taking advantage of relatively low labour costs. The service sector is likely expanding to cater for an emerging middle class of consumers.
|
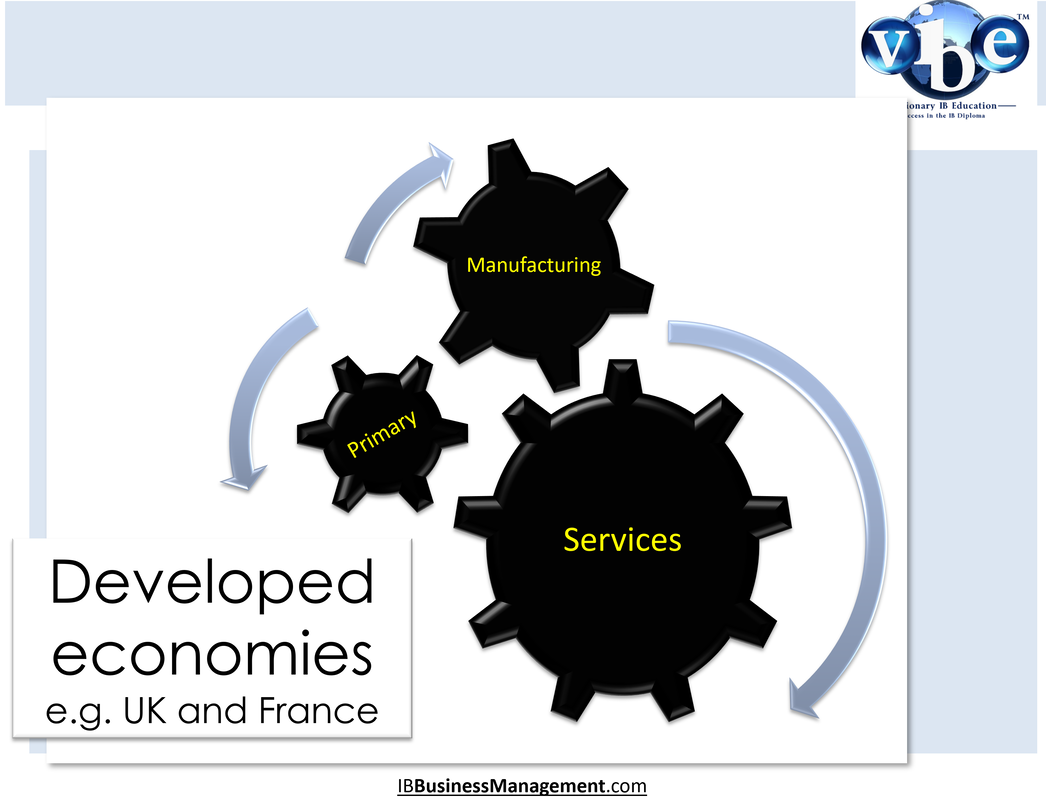
Developed economiesDeveloped economies (e.g. the UK) will be primarily service sector focused. The majority of businesses and people employed by businesses will be operating in the service industries. The provision of services is generally and relatively more profitable as services are often purchased on a continual basis by the consumer (e.g. internet and pay television).
|
IB Business Management 1.1 WHAT IS A BUSINESS?
SUMMARY NOTES
IB Business Management: 1.1 What is a business? teaching and learning PowerPoint notes for HL and SL IB Business Management
PROGRESS CHECK – Test your understanding by completing the activities below
You have a range of practice activities, interactive flash cards, exam practice questions, interactive quizzes and classroom games to ensure you and your students have complete mastery of the IB Business Management requirements for the 1.1 Introduction to business topic.
USE THE FLASHCARDS IN ALL STUDY MODES
|
IB Business Management
1.1 What is a business? Student learning activity A
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
|
IB Business Management
1.1 What is a business? Student learning activity B
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
|
|
IB Business Management
1.1 What is a business? Student learning activity C
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
|
IB Business Management
1.1 What is a business? Exam practice questions
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
|
IB Business Management interactive quizzes and classroom games
Test how well you know the IB Business Management Introduction to Business Management: What is a business? topic with the interactive self-assessment quizzes below. Each interactive quiz selects 30 questions at random from a larger question bank so keep on practicing! Aim for a score of at least 80 percent.
|
Loading 1.1A What is a business?
|
Loading 1.1B What is a business?
|