|
IB Business Management:
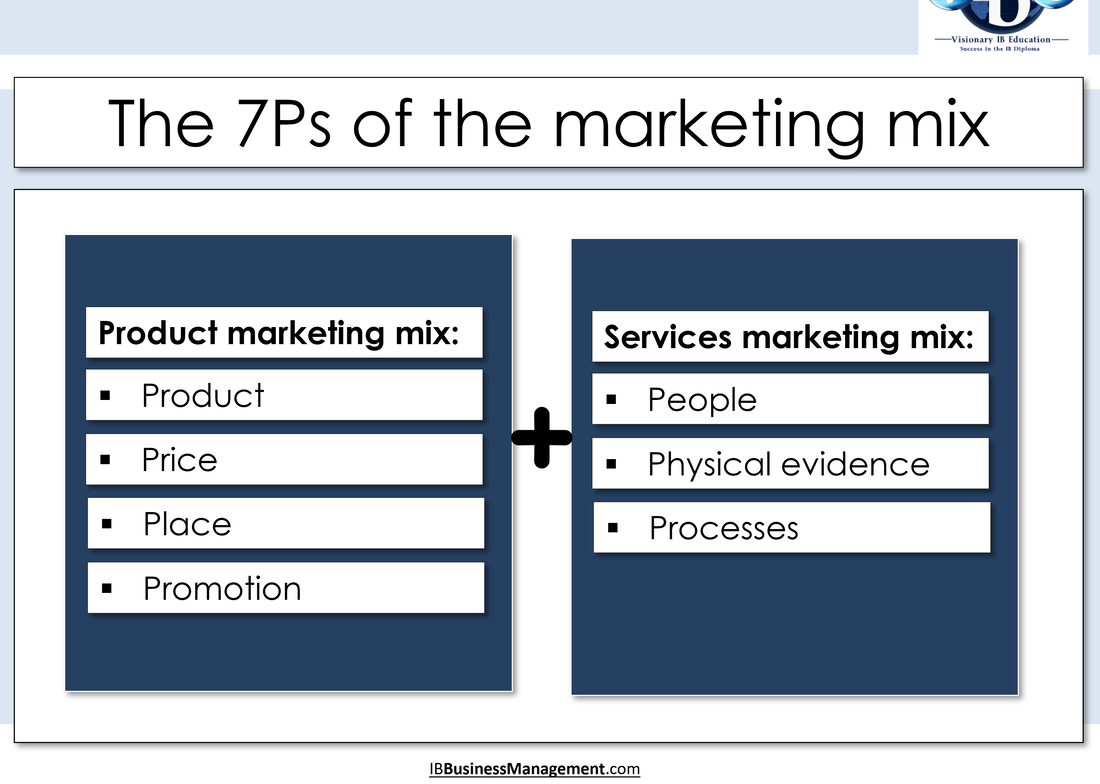
4.4 7Ps of the marketing mix Marketing is the management task that links the business to the customer by identifying and meeting the needs of customers profitably – it does this by promoting the right product at the right price at the right place to the right customers. The marketing department of any organisation will have an integrated strategy or strategies regarding the marketing mix – the 4 Ps of Product, Price, Place and Promotion; and an additional 3Ps are part of an integrated marketing mix for services: People, Processes and Physical evidence.
|
Key learning outcomes:There are too many specific learning outcomes for Topic 4.4 The 7Ps of the marketing mix to outline all of them here.
The 7 Ps of the marketing mix is the largest single-section of the IB Business Management course and, as such, we are devoting an entire page to each element of the traditional marketing mix (the 4Ps), where the learning outcomes are separated out into sub-topics: We then turn our attention to the marketing of services, and the additional three Ps: People, Processes and Physical evidence |
The marketing mixMarketing mix: The key decisions that must be taken in the effective marketing of a product.
The marketing mix is made up of seven interrelated decisions − the 7Ps. The four key ones are product, price, promotion (including advertising and packaging) and place (where and how a product will be sold to consumers).
The other 3Ps largely relate to the marketing of services – people, process and physical evidence. The marketing mix:
|
The integrated marketing mixNot all of the 7Ps have the same degree of significance in every case. It is vital that these elements fit together into a coherent and integrated plan. An appropriate marketing mix will ensure that these marketing decisions are interrelated. They must be carefully coordinated to make sure that customers are not confused by conflicting messages being given about the good or service being sold.
Coordinated marketing mix: Key marketing decisions complement each other and work together to give customers a consistent message about the product. If just one part of the marketing is inconsistent or does not integrate with the rest, it may lead to the failure of even the best marketing plan. The most appropriate marketing mix decisions will therefore be:
The 7Ps of the marketing mix explained |