|
IB Business Management:
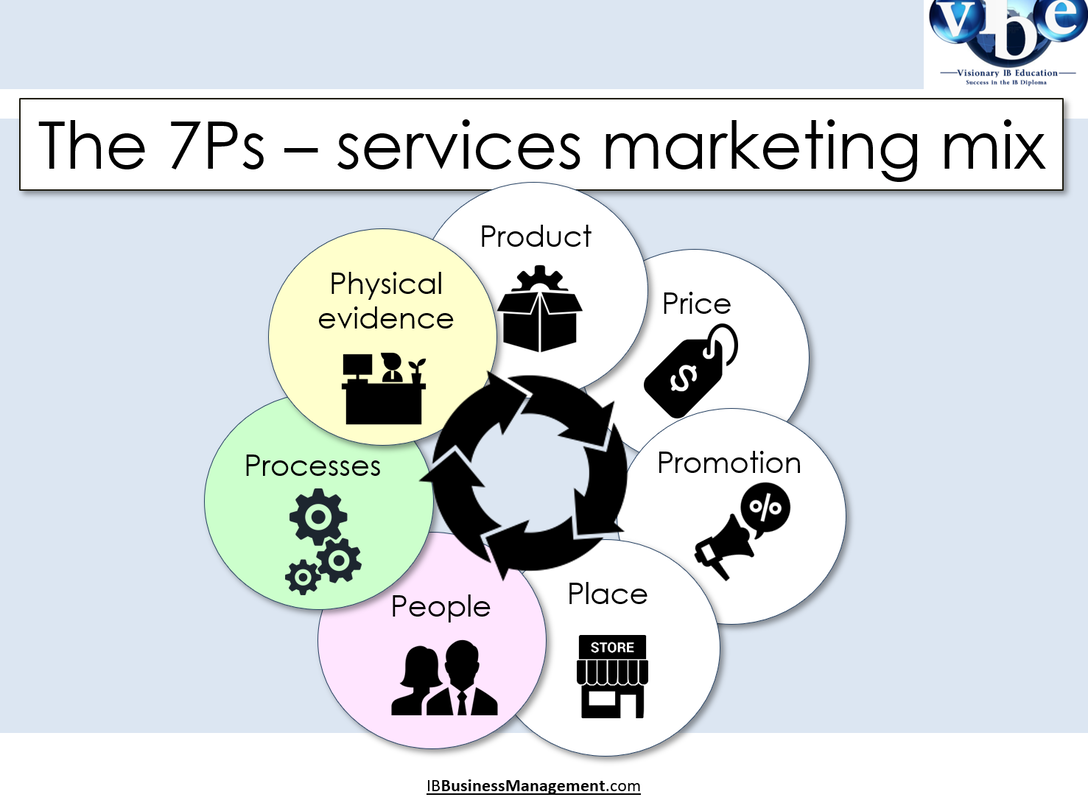
4.4 The 7Ps marketing mix The traditional marketing mix consists of the '4 Ps': Product, Price, Place and Promotion. The extended marketing mix includes an addition three components: Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Processes and Physical evidence – the 7Ps. The extended marketing mix targets a more customer orientated approach to marketing and is now integral in the marketing of services.
|
Key learning outcomes:
|
The marketing of servicesThe 7 Ps in a service-based market
The marketing mix for a product is a major factor in influencing whether a business can sell it profitably. The marketing mix is the key decisions that must be taken in the effective marketing of a product.
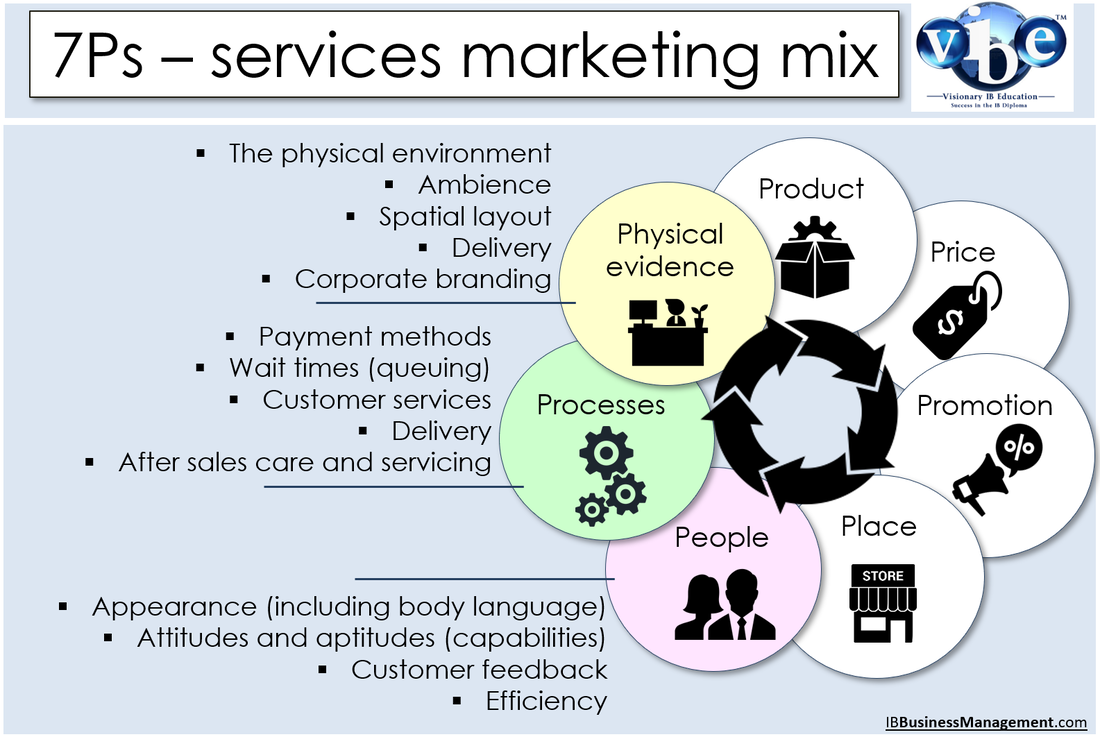
The extended marketing mix – the seven Ps model – is made up of seven interrelated decisions − the 7Ps. The four key ones are product, price, promotion (including advertising and packaging) and place (where and how a product will be sold to consumers). The other 3Ps largely relate to marketing services – people, process and physical evidence.
Not all of the 7Ps have the same degree of significance in every case. It is vital that these elements fit together into a coherent and integrated plan. An appropriate marketing mix will ensure that these marketing decisions are interrelated. They must be carefully coordinated to make sure that customers are not confused by conflicting messages being given about the good or service being sold. Coordinated marketing mix: The key marketing decisions complement each other and work together to give customers a consistent message about the product. |
The 7Ps of the services marketing mixAn introduction to the 7 PsKey termsThe marketing mix: The marketing mix refers to the set of actions, or tactics, that a company uses to promote its brand or product in the market. It is a planned mix of the controllable elements of a product's marketing plan and is commonly termed as the 4Ps: product, price, place, and promotion.
Services: A service is an intangible (unable to be touched; not having physical presence) product supplied by an organisation; examples include: haircuts, photography, banking, insurance, transport, repairs and maintenance. The extended marketing mix (the seven Ps model): This applies to the marketing mix associated with services delivery. It encompasses the 4 Ps of the traditional marketing mix (Product, Price, Place and Promotion) and includes an additional three Ps: (People, Processes and Physical Evidence. The additional Ps have been added because today marketing is far more customer oriented than ever before, and because the service sector of the economy has come to dominate economic activity in this country. These 3 extra Ps are particularly relevant to this new extended service mix. |
How not to do services marketing! |
UK services marketing – 5 peculiar British problems!“Having my haircut, the barber said 'Is that alright?” I nodded, but it wasn’t.” “I phoned Netflix customer support which is US based, they were so overly polite I thought they were being sarcastic and hung up.” “Heard an announcement at the train station. “We are sorry.” Just that, nothing else.” “A man in the supermarket was browsing the food I wanted to browse, so I had to pretend to look at things I didn’t even want until he left.” “I accidentally rang the bell on the bus at the wrong stop and instead of explaining my predicament to the driver, got off and walked the rest of the way home." |
PeopleProviding a service depends heavily on the goodwill of a business’s employees. Hospitals require doctors and nurses who are caring and committed to helping patients recover. Schools need effective, competent and passionate teachers to provide effective student education. Friendly and helpful hotel staff will ensure that guests have the best possible experience and are likely to be repeat customers and recommend the hotel to family, friends and acquaintances – perhaps even writing a positive online review that will reach and influence thousands of potential customers.
It is essential for service providers to form effective employee-customer service relationships in the marketing of their product. The effectiveness of an organisation’s people in delivering or marketing a service can be measured in four ways:
Six dimensions of organisational culture |
Cultural variation in employee-customer relationshipsCultural variation plays a significant role in shaping the employee-customer relationship. This relationship is influenced by factors such as cultural norms, values, communication styles, and expectations of both the employees and customers. Here, we will examine some ways in which cultural variation can affect the employee-customer relationship across different countries:
These examples highlight some of the ways in which cultural variation can impact the employee-customer relationship. Understanding and adapting to these differences is crucial for businesses aiming to provide effective customer service and succeed in diverse global markets. |
ProcessesProcesses refer to the particular methods of delivering or providing a service. Processes will include: customer services practices and procedures, methods of paying, delivery methods, after sales care, wait times, etc. It is far easier to show a potential customer a product when explaining it, whereas explaining different mortgage options or investment vehicles in banking services can be quite complex for a customer to understand.
Processes in services marketing are important because an effective service-orientated business will have significant repeat purchases from their customers. For example, a hair salon that only sees a customer only once is a hair salon that will not be in business very long! Customers who experience excellent customer service and care are those who will both return and provide valuable word-of-mouth promotion to family and friends, as well as increasingly important social networks. The different processes involved in services marketing include:
More on the 7 Ps of servicing marketingThe 7 Ps – Apple vs. Pound Land |
Physical evidencePhysical evidence plays an important role in the extended marketing mix for services. Services as we know are largely intangible when marketing. However customers tend to rely on physical cues to help them evaluate the product before they buy it. Therefore marketers develop what we call physical evidence to replace these physical cues in a service. The role of the marketer is to design and implement such tangible evidence. Physical evidence is the material part of a service and will include aspects such as the physical environment, ambience, spatial layout and corporate branding.
|
The effect of changes in delivery processes in the marketing of servicesChanges in delivery processes have had significant effects on the marketing of services in recent years. Here are some real-world examples to illustrate how these changes have impacted businesses:
These real-world examples demonstrate how changes in delivery processes have significantly impacted the marketing of services across various industries. Adapting to these changes and incorporating them into marketing strategies has become crucial for businesses to remain competitive and meet customer expectations. |
The significance of tangible physical evidence in service marketingTangible physical evidence plays a crucial role in service marketing, as it helps customers evaluate and perceive the quality of services being offered. Physical evidence can create a lasting impression and contribute to the overall customer experience. Here are some real-world examples to illustrate the significance of tangible physical evidence in service marketing:
These examples emphasise the importance of tangible physical evidence in service marketing. By investing in high-quality physical evidence, businesses can create a positive and lasting impression on customers, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. |
IB Business Management 4.4e The 7 Ps of the services marketing mix
SUMMARY NOTES
IB Business Management: 4.4e The 7 Ps of the services marketing mix teaching and learning PowerPoint notes for HL and SL IB Business Management
PROGRESS CHECK – Test your understanding by completing the activities below
You have a range of practice activities, interactive flash cards, exam practice questions, interactive quizzes and classroom games to ensure you and your students have complete mastery of the IB Business Management requirements for the 4.4e The 7 Ps of the services marketing mix topic.
USE THE FLASHCARDS IN ALL STUDY MODES
|
IB Business Management
4.4e The 7 Ps of the services marketing mix Student learning activity Q
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
|
IB Business Management
4.4e The 7 Ps of the services marketing mix Exam practice question
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
|
IB Business Management interactive quizzes and classroom games
Test how well you know the IB Business Management The 7 Ps of the services marketing mix topic with the interactive self-assessment quizzes below. Each interactive quiz selects 30 questions at random from a larger question bank so keep on practicing! Aim for a score of at least 80 percent.